Join a free live demo now!
See all features live
Understand the benefits
Get your questions answered
No purchase pressure
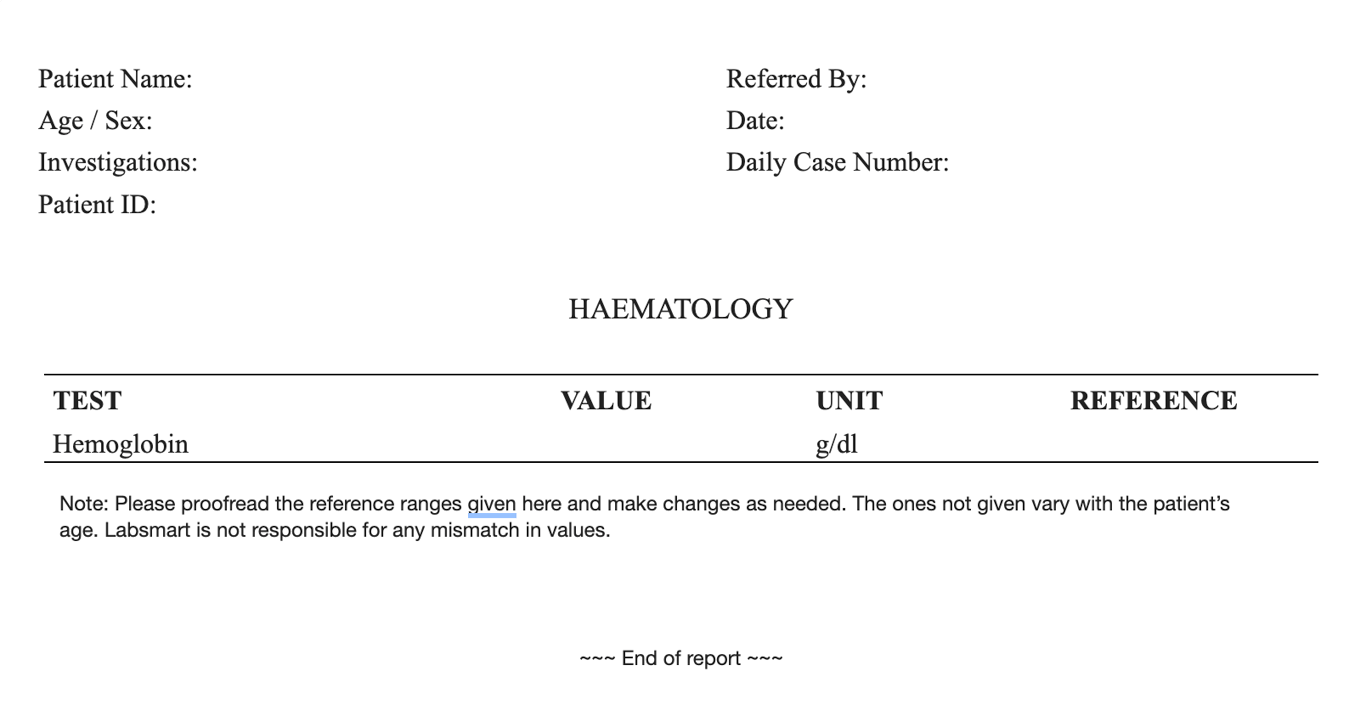
What is Hemoglobin (Hb) ?
Before going deep into the report, let’s break down what hemoglobin is. Hemoglobin is a protein in our red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout our body. Low or high levels of hemoglobin can indicate various health conditions, making it a critical metric in blood tests.
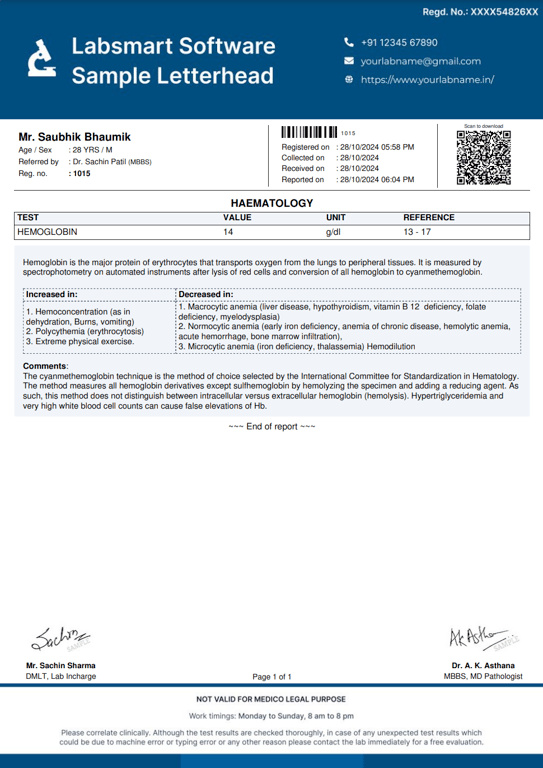
Hemoglobin (Hb) Report Format: Breakdown
The hemoglobin report is often part of a Complete Blood Count (CBC). But hemoglobin test is also done individually much more frequently and here’s what a hemoglobin report format consists of:
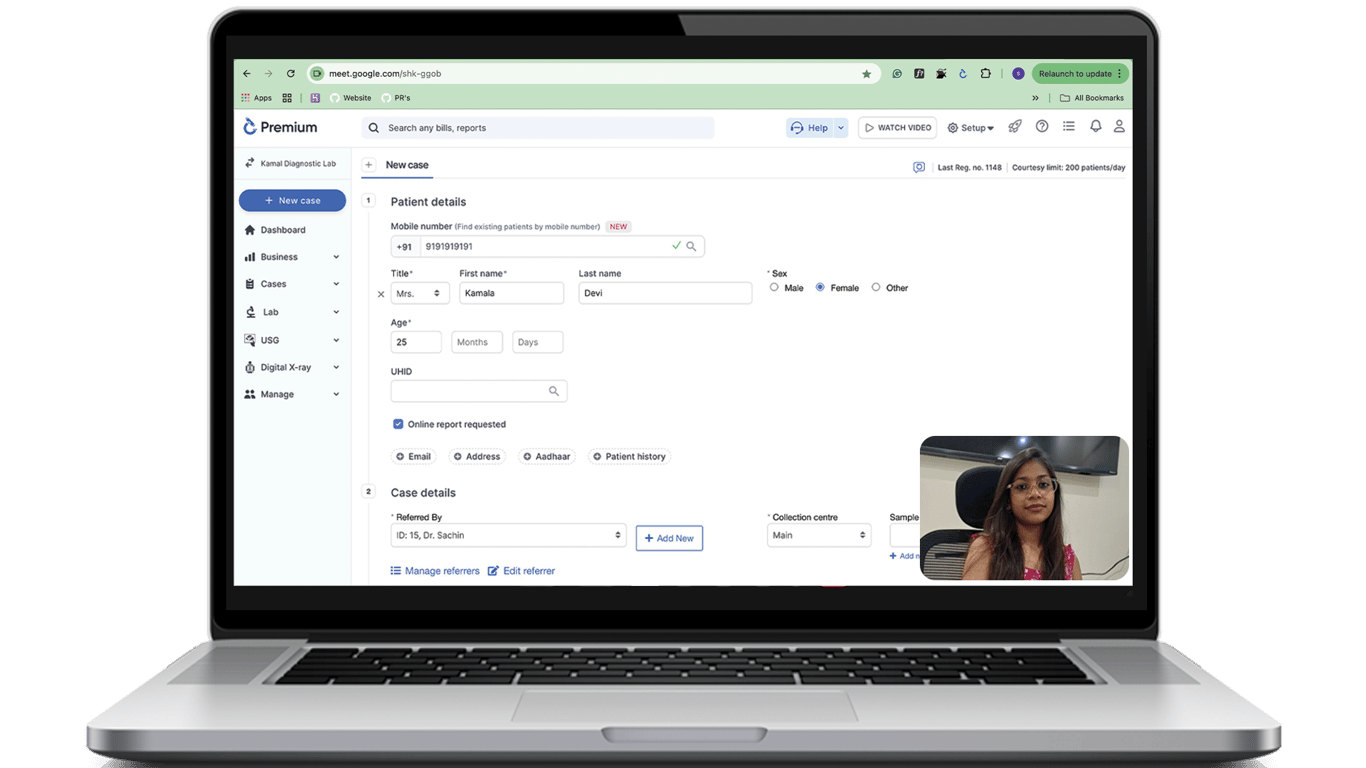
Header Information:
- Patient Details: Full name, Age, Gender, and ID.
- TAT information: Timestamp for both sample collection and report generation.
- Doctor's Information: Name of the referral doctor, if applicable.
Test Results Section:
-
Patient's results
As obvious as it is, a test report should definitely have the patient's test result.
-
Result's Unit
The unit of the test result must be mentioned correctly in the report. Hemoglobin (Hb) test is generally reported in “g/dl”
-
Hemoglobin (Hb) Normal Value / Reference Range
The report must have the normal Hemoglobin (Hb) range. It can differ slightly based on the reagents used by the lab and other internal factors, but common Hemoglobin (Hb) ranges are:
For any gender, 0 to 21 days of age: 17 - 23 g/dl For any gender, 21 days to 10 years of age: 11.2 - 16.5 g/dl For males, 10 to 100 years of age: 13 - 17 g/dl For females, 10 to 100 years of age: 12 - 15 g/dl
Interpretations
Nowadays, most labs prefer to add interpretations to the reports, making the report more patient-friendly. Labsmart software has interpretations of all routine test pre-filled in the software.
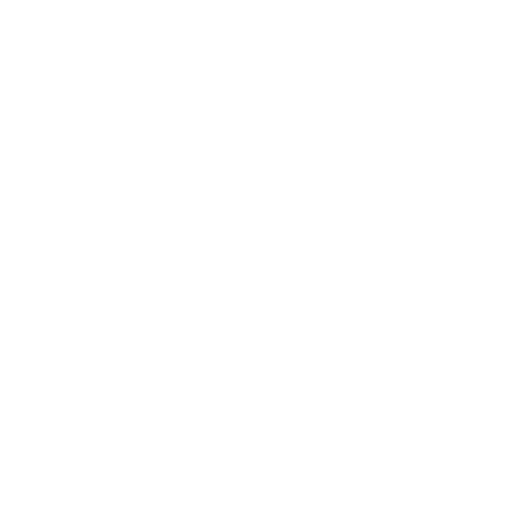
Footer Section:
-
Certifications:
Display any relevant accreditations (e.g., NABL, ISO), adding to your lab's credibility.
-
Pathologist and technician signature:
It's mandatory to add a Pathologist and technician signature to the report.
Hb Interpretation
In Labsmart software, this is the inbuilt interpretation for Hemoglobin (Hb)
Importance of adding interpretation to reports:
It's very helpful to add interpretation in reports as it makes the reports more patient friendly and also helpful to doctors in some cases. Moreover, presently most labs prefer providing reports with interpretation. Thus, adding interpretation to report will help your lab stay at par with other competitor labs.
Labsmart Pathology Reporting Software
(With Interpretation and auto calculations)
- Billing
- Reports with Interpretation
- Auto calculation where needed
- Check daily business
- WhatsApp reports
1.5 Crore+
Reports printed & delivered online
1250+
Labs Active
10+
Countries
Hb MS Word format
Download the Ms word editable Hemoglobin (Hb) report format for offline reporting.
Download word format